Caring for Your Feline Friend: Understanding and Treating Chronic Kidney Disease in Cats


As a devoted cat parent, you want nothing more than to ensure your cat’s well-being. However, just like humans, cats can develop various health conditions, and one of the most common is chronic kidney disease (CKD).
This progressive condition affects your cat’s ability to filter waste products from the blood, leading to a gradual decline in kidneys and affecting their quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of chronic kidney disease in cats, equipping you with the knowledge to provide the best possible care for your furry companion.
Understanding the Types, Causes, and Risk Factors of Chronic Kidney Disease in Cats
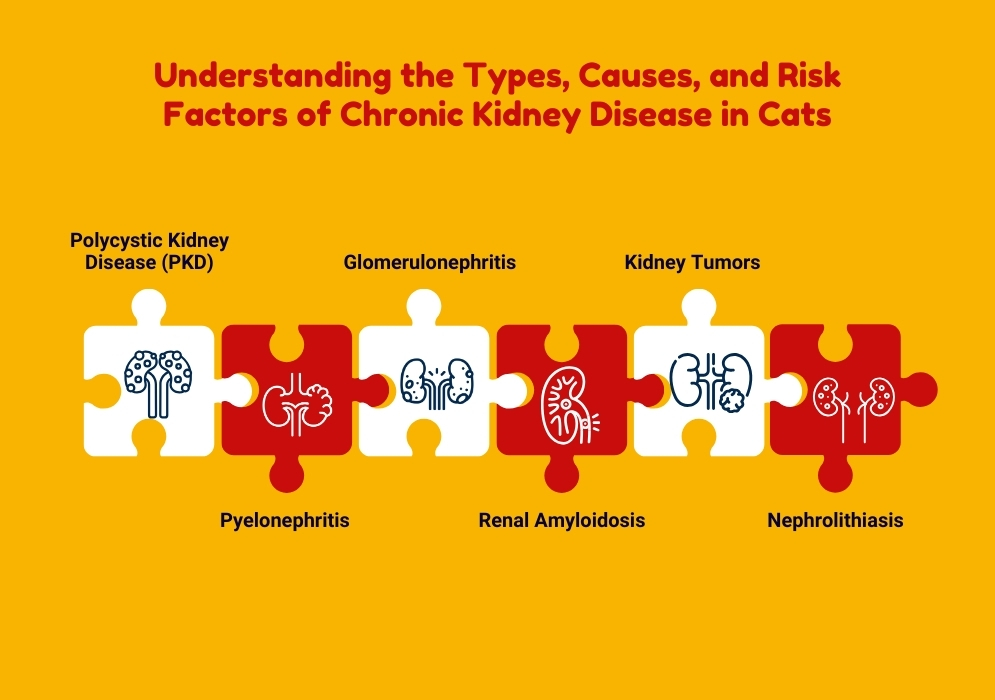
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in cats can result from various underlying conditions. Here are some common types:
- Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD): This is an inherited condition, particularly prevalent in Persian and related breeds, where multiple fluid-filled cysts replace normal kidney tissue.
- Pyelonephritis: This is a bacterial infection of the kidneys that can cause significant damage and lead to CKD.
- Glomerulonephritis: This involves inflammation and damage to the kidney’s filtration membrane.
- Renal Amyloidosis: This condition involves the buildup of an abnormal protein in the kidneys, impairing their function.
- Kidney Tumors: Various tumors, such as lymphoma, can affect the kidneys and lead to CKD.
- Nephrolithiasis: This refers to kidney stones, which can cause blockages and damage the kidneys.
Potential Causes of Kidney Diseases in Cats
To effectively manage chronic kidney disease in cats, it’s essential to understand the underlying causes and risk factors. By being aware of these factors, you can take preventive measures and make informed decisions about your cat’s care. Potential causes of chronic kidney disease in cats include:
- Age: As cats age, their kidneys naturally gradually decline in function, making them more susceptible to chronic kidney disease.
- Genetics: Certain breeds, such as Persians and Siamese, may have a higher predisposition to developing kidney problems.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can damage the kidneys and contribute to the development of chronic kidney disease.
- Toxin exposure: Exposure to certain toxins, such as antifreeze, household cleaners, or certain medications, can lead to kidney damage.
- Dental disease: Poor dental hygiene and periodontal disease can allow bacteria to enter the bloodstream,potentially affecting the kidneys.
Risk Factors
Additionally, several risk factors can increase the likelihood of your cat developing chronic kidney disease:
- Dehydration: Inadequate water intake can strain the kidneys and exacerbate the condition.
- High-protein diet: Excessive protein consumption can put additional stress on the kidneys, potentially accelerating the progression of the disease.
- Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to various health issues, including kidney disease.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to kidney damage over time.
By being mindful of these causes and risk factors, you can take proactive steps to minimize the chances of your cat developing chronic kidney disease or to slow its progression if it does occur.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease in Cats
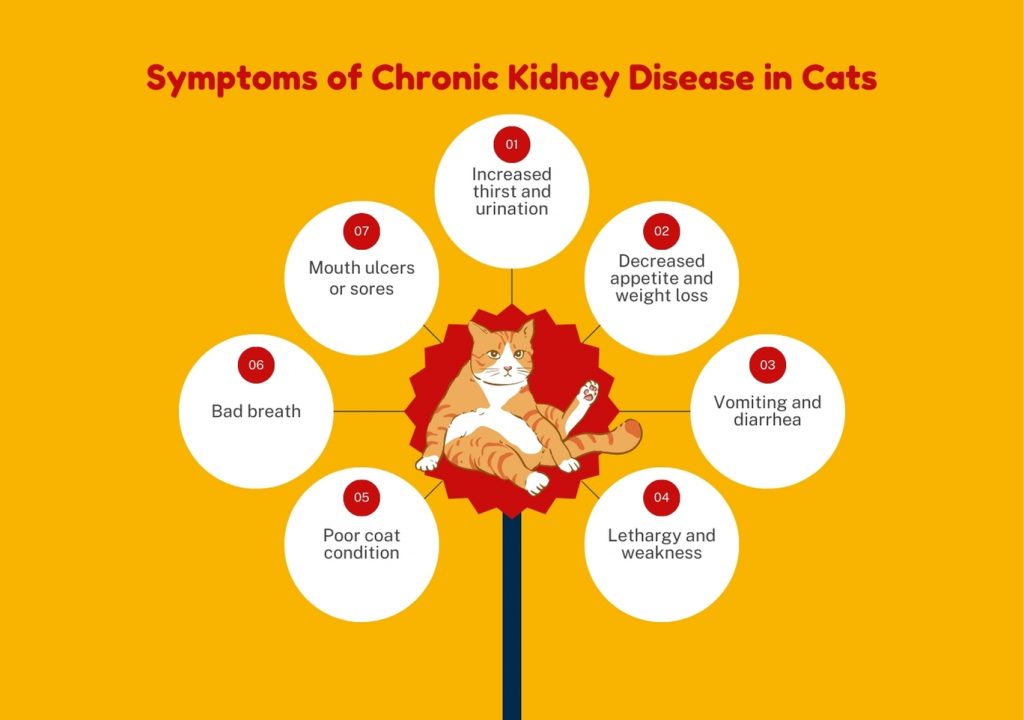
Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial in managing chronic kidney disease in cats. By familiarizing yourself with the common symptoms, you can identify potential issues and seek veterinary care promptly. Common symptoms of chronic kidney disease in cats include:
- Increased thirst and urination: As the kidneys struggle to filter waste products effectively, your cat may drink more water and urinate more frequently.
- Decreased appetite and weight loss: Cats with chronic kidney disease may experience a loss of appetite and subsequent weight loss due to the buildup of toxins in the body.
- Vomiting and diarrhea: The accumulation of waste products can cause gastrointestinal issues, leading to vomiting and diarrhea.
- Lethargy and weakness: As the disease progresses, your cat may become increasingly lethargic and weak due to the buildup of toxins and the strain on the body.
- Poor coat condition: Chronic kidney disease can lead to a dull, unkempt coat as due to poor nutrient absorption and dehydration.
- Bad breath: The buildup of waste products in the body can cause an unpleasant odor, resulting in bad breath.
- Mouth ulcers or sores: In some cases, chronic kidney disease can lead to the development of mouth ulcers or sores.
It’s important to note that some of these symptoms can also indicate other health conditions. If you notice any of these signs in your cat, seek prompt veterinary attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease in Cats: Tips for a Healthy Lifestyle

While chronic kidney disease in cats cannot be entirely prevented, several proactive steps can be taken to minimize the risk and promote overall kidney health.
Maintain a healthy weight
Obesity can put additional strain on your cat’s kidneys and contribute to the development of various health issues, including chronic kidney disease. Work with your veterinarian to ensure your cat maintains a healthy weight through proper diet and exercise.
Provide adequate hydration
Proper hydration is crucial for kidney health. Ensure your cat has access to fresh, clean water at all times, and consider incorporating wet food or broths into their diet to increase their fluid intake.
Choose a high-quality, balanced diet
A well-balanced diet, rich in essential nutrients and appropriate protein levels, can support kidney health and overall well-being. Consult your veterinarian to determine the best diet for your cat’s specific needs.
Promote dental health
Poor dental hygiene and periodontal disease can contribute to the development of chronic kidney disease. Regular dental check-ups and at-home dental care, such as brushing or providing dental treats, can help maintain good oral health.
Minimize exposure to toxins
Certain household chemicals, medications, and toxins can be harmful to your cat’s kidneys. Keep these substances out of reach and follow proper storage and disposal guidelines.
Schedule regular veterinary check-ups
Regular check-ups with your veterinarian can help detect potential health issues, including chronic kidney disease, in the early stages when they are more manageable.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can proactively support your cat’s kidney health and potentially reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney disease or slowing its progression.
Clinical treatment for cats suffering from kidney Disease
There are several clinical treatments available for cats suffering from chronic kidney disease (CKD). One of the most common treatments is fluid therapy. This can include intravenous (IV) fluids for acute cases or subcutaneous (under the skin) fluids for chronic management to help maintain hydration.
Moreover, depending on which stage of kidney disease your cat is in, your vet may also suggest a combination of medications. Some of the common ones that your vet may suggest are:
- Telmisartan (Semintra): An angiotensin II receptor blocker used to manage hypertension and proteinuria in cats with CKD.
- Capromorelin (Elura): A ghrelin receptor agonist that helps stimulate appetite and support weight gain.
- Phosphate Binders: These help reduce phosphate levels in the blood, which can be elevated in CKD.
- Anti-nausea medications, such as maropitant (Cerenia), are used to manage nausea and vomiting.
Providing Supportive Care for Cats with Chronic Kidney Disease
In addition to medical treatments, providing supportive care is crucial for improving your cat’s quality of life and managing the symptoms of chronic kidney disease.
Environmental management
Create a comfortable and stress-free environment for your cat. Minimize potential stressors, such as loud noises or changes in routine, as stress can exacerbate the symptoms of chronic kidney disease.
Warmth and comfort
Cats with chronic kidney disease may feel colder due to poor circulation and dehydration. Provide warm, cozy bedding, and consider using heating pads or heated beds to help keep your cat comfortable.
Litter box management
Increased urination is a common symptom of chronic kidney disease. Ensure your cat can easily access multiple clean litter boxes to accommodate their needs and minimize stress.
Nutritional support
If your cat is experiencing a decreased appetite or difficulty eating, consider offering high-calorie supplements or nutrient-dense foods to help maintain their weight and overall health.
Hydration support
In addition to encouraging water intake, you may need to provide supplemental hydration through subcutaneous fluids or other methods, as your veterinarian recommends.
Pain management
Chronic kidney disease can be accompanied by discomfort or pain. Your veterinarian may prescribe pain medications or recommend alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or massage, to help alleviate your cat’s discomfort.
Remember, early detection and intervention are crucial in managing chronic kidney disease. Regular veterinary check-ups, dietary modifications, fluid therapy, and appropriate medications can help slow the progression of the disease and alleviate its symptoms.
Providing supportive care, such as a comfortable environment, nutritional support, and pain management, can also greatly improve your cat’s quality of life.
Additionally, monitoring your cat’s condition and making necessary adjustments to their treatment plan can ensure they receive the best possible care throughout their journey.









Leave A Comment