What’s Beneath The Fur: A Look At German Shepherd Skeleton


Are you a parent of a German Shepherd dog? Then you may have wondered once or twice (probably during an intense game of fetch) what makes them so strong, agile, and athletic. To find out, you need to learn more about the German Shepherd skeleton system, which provides the framework for their strength, agility, and endurance.
In this article, we will explore the key features of the German Shepherd skeleton, explaining how they contribute to the breed’s exceptional physical abilities. We will also highlight any breed-specific health concerns due to the German Shepherd’s skeleton structure. Let’s get started.
Understanding The Anatomy Of A German Shepherd
The German Shepherd is a breed of dog that is known for its intelligence, loyalty, and versatility. Originally developed in Germany for herding sheep, this breed has since become one of the most popular in the world. German Shepherds are highly trainable and adaptable. Moreover, they are also eager to please. Which is why, these dogs have been successfully employed in various roles, including search and rescue, police work, and as guide dogs for the visually impaired.

To truly appreciate the remarkable abilities of the German Shepherd, it is important to understand its anatomy. This breed has a well-balanced and powerful body that allows it to perform a wide range of tasks. From its muscular build to its strong skeletal structure, every aspect of the German Shepherd’s anatomy is designed for efficiency and agility. Lets take a look:
The Physical Structure Of A German Shepherd
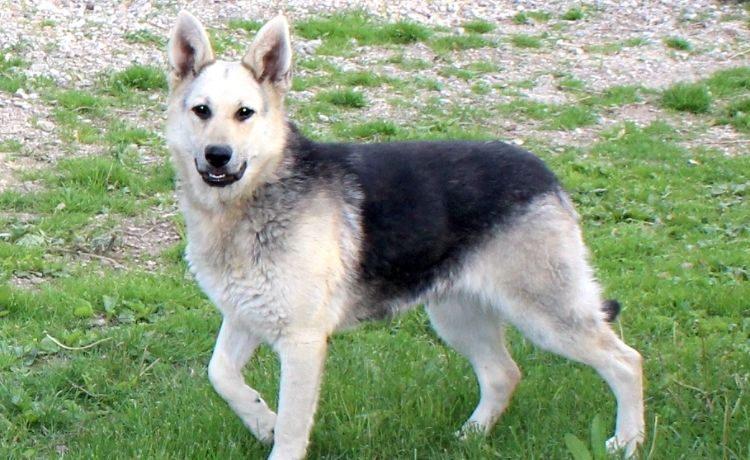
The German Shepherd’s physical structure is one of its defining features. It is built for strength, agility, and endurance. The breed has a straight back and a deep chest, which contribute to its overall balance and stability.
Its legs are straight and parallel, providing a solid foundation for its body. Its hindquarters are well-developed, giving it the ability to generate powerful forward propulsion. These features, combined with its flexible spine and well-articulated joints, allow the German Shepherd to move with ease and grace.
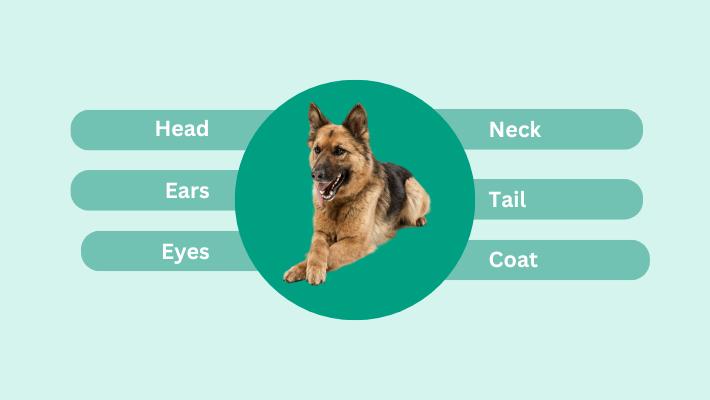
- Head: The head is wedge-shaped, with a strong muzzle and well-defined stop. The teeth meet in a scissors bite, meaning the incisors of the lower jaw meet just inside the incisors of the upper jaw.
- Ears: The ears are erect and triangular, set high on the head. They are firm and alert, giving the German Shepherd a watchful expression.
- Eyes: The eyes are almond-shaped and brown or black. They are intelligent and alert, reflecting the German Shepherd’s working nature.
- Neck: The neck is strong and muscular, allowing the German Shepherd to carry its head high and proud.
- Tail: The tail is bushy and reaches to the hock joint. It is held low when relaxed and raised high when excited or alert.
- Coat: The German Shepherd has a double coat, which is medium to long in length. The outer coat is dense and weatherproof, while the undercoat is soft and insulating.
Key Features Of The German Shepherd’s skeleton
The German Shepherd’s skeleton is built to withstand rigorous activity and stress. Its bones are dense and strong, providing support and protection for its internal organs. The breed has a well-developed ribcage, which houses its vital organs and provides additional stability to its body. We have explained them in detail below:

Skull:
It is broad and proportionate to its body size, accommodating its powerful jaws and teeth. The German Shepherd’s teeth are sharp and strong, allowing it to effectively grip and hold onto objects.
Spine:
The spine is made up of vertebrae, which provide flexibility and support for the body. The German Shepherd has 7 cervical vertebrae in the neck, 13 thoracic vertebrae in the chest (connected to the ribs), lumbar vertebrae in the lower back, and a sacrum and coccyx in the tail.
Ribs:
The ribs are flat bones that connect the spine to the sternum (breastplate) and protect the heart, lungs, and other vital organs.
Shoulder assembly:
The shoulder assembly is a complex joint that allows for a wide range of motion in the front legs. It’s formed by the scapula (shoulder blade), humerus (upper arm bone), radius and ulna (lower leg bones), and carpus (wrist).
Pelvis:
The pelvis is a bony structure that supports the rear legs and internal organs. It’s made up of the ilium, ischium, and pubis bones.
Legs:
The legs are long and powerful, with strong bones and well-developed muscles. The femur (thigh bone), tibia and fibula (shin bones), and tarsus (hocks) make up the rear legs, while the scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, and carpus form the front legs.
The paws have metacarpals (in the front) and metatarsals (in the back) in the legs, leading to the phalanges (toes). The angulation of the front and rear legs is crucial for efficient movement. The German Shepherd has a moderate angulation that allows for both stability and flexibility.
The Muscular System Of A German Shepherd
The muscular system of a German Shepherd is just as impressive as its skeletal structure.These dogs are working breeds and their muscles reflect that, with a powerful and well-developed musculature throughout their entire body. Here’s a breakdown of the key muscle groups:

Head and Neck: Powerful muscles in the jaw allow for a strong bite force. Muscles in the neck support the head and allow for flexibility and range of motion.
Forelimbs: The shoulders have strong muscles that power the front legs for activities like digging and pulling. Muscles in the forearms and paws allow for flexion and extension of the legs for running and jumping.
Core: The core muscles, including the rectus abdominus, obliques, and transversus abdominus, provide stability and support for the spine and internal organs. Strong core muscles are essential for powerful movement and proper posture.
Hindlimbs: The hindlimbs are the powerhouse of the German Shepherd’s body. Powerful muscles in the thighs and buttocks provide propulsion for running and jumping. However, the muscles in the lower legs and paws allow for flexion and extension of the legs for powerful strides.
Back: Strong muscles along the back, including the latissimus dorsi and longissimus dorsi, support the spine and provide power for movement. These muscles also help with tasks like carrying objects and maintaining balance.
How The German Shepherd’s Anatomy Contributes To Its Unique Abilities
The German Shepherd’s anatomy plays a crucial role in its unique abilities. Here’s how each aspect contributes to their unique abilities:

Strength And Endurance
- Skeleton: The strong bones and well-developed joints provide a stable platform for powerful muscles. The moderate angulation in their legs allows for both stability and flexibility, crucial for tasks requiring agility and endurance.
- Muscles: Powerful muscles throughout their body, especially in the hind limbs and core, give them the strength for tasks like pulling, carrying objects, and leaping fences. Their well-developed core also provides stability and allows them to maintain proper posture during strenuous activity.
Speed And Agility
- Skeleton: The long, strong legs allow for powerful strides when running. The flexible spine and well-angled joints allow for quick changes in direction and maneuvering in tight spaces.
- Muscles: Powerful muscles in the forelimbs and hindlimbs provide the explosive power needed for running, jumping, and changing direction quickly.
Alertness And Intelligence
- Head: The strong jaw muscles allow for a powerful bite, important for protection work. Keen eyesight and hearing are aided by the position and shape of the eyes and ears.
- Brain: German Shepherds are bred for intelligence and trainability. Their well-developed brain allows them to learn complex commands and excel in tasks requiring problem-solving and critical thinking.
Double Coat
- Provides protection: The dense outer coat protects them from harsh weather conditions, scratches, and bites during working situations.
- Temperature regulation: The undercoat insulates them in cold weather and helps regulate their body temperature in hot weather. This allows them to perform effectively in various climates.
Common Health Issues Related To The German Shepherd’s Anatomy
While the German Shepherd is a robust and resilient breed, it is not without its share of health issues. Here are some common health problems related to their anatomy:

Hip And Elbow Dysplasia:
These are hereditary conditions where the joints don’t develop properly. The shallow hip sockets or malformed elbow joints cause pain, instability, and eventually arthritis due to abnormal wear and tear. Their large size and deep chest contribute to these conditions.
Degenerative Myelopathy (DM)
This progressive neurological disease affects the spinal cord, causing weakness and incoordination in the hind legs. It’s particularly troubling as it affects them in their senior years.
Bloat (Gastric Dilatation And Volvulus)
Their deep chest cavity creates space for the stomach to twist and bloat, potentially cutting off blood flow and causing a life-threatening emergency.
Perianal Fistula
German Shepherds are prone to inflamed tracts near the anus due to the pressure placed on the area by their anatomy. This can be very painful and requires veterinary attention.
Arthritis
With age and the stress placed on their joints, especially those predisposed to dysplasia, German Shepherds are more likely to develop arthritis.
Being aware of the signs of hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia, and DM allows for early intervention which can improve their quality of life. In addition, having an understanding of their anatomy can also help with preventive care.
Proper Care And Maintenance Of A German Shepherd’s Anatomy
To ensure the well-being of a German Shepherd’s anatomy, proper care and maintenance are essential. Here are some tips on how you can take good care of your German Shepherd:

Training And Exercise Considerations For A German Shepherd’s Anatomy
Proper Training and exercise play a significant role in the development and well-being of a German Shepherd’s anatomy. Regular exercise strengthens muscles which support the joints and improves overall health. Opt for walks, jogging (once fully grown), swimming, and obedience training for mental stimulation. However, avoid strenuous activities like jumping from heights while they’re young and growing to minimize strain on developing joints.
Mental stimulation, such as puzzle toys and training exercises, can help keep their minds sharp and prevent boredom.
Warm-Up And Cool-Down
Before strenuous activities, include a light warm-up (walking) to prepare muscles and joints. Similarly, incorporate a cool-down (walking) to prevent post-exercise stiffness.
Proper Lifting
German Shepherds are large dogs, but avoid letting them jump on furniture. Use ramps or steps to minimize stress on their hips and joints. If lifting them is necessary, support their weight evenly.
Diet And Weight Management
Provide a high-quality diet formulated for large breed dogs to ensure proper nutrition for bone and muscle development. This is because a balanced diet with proper joint supplements can help promote healthy cartilage and slow the progression of arthritis and help keep the German Shepherd skeleton in good condition. It will also help them to maintain a healthy weight which will minimize stress on joints, especially hips and elbows.
Joint Supplements
Glucosamine and chondroitin are the two most common ingredients in joint supplements. They are natural substances that help to rebuild cartilage and reduce inflammation. In addition to these two components, you can also look for supplements that contains the following ingredients:
- MSM (methylsulfonylmethane) is a sulfur compound that helps to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce joint pain and inflammation. They also support the health of the cartilage in the joints. Fish oil is a good source of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Hyaluronic acid is a substance that is available naturally in the joints. It helps to lubricate the joints and keep them moving smoothly.
However, you should talk to your veterinarian before giving your German Shepherd any joint supplements. They can help you choose the right supplement for your dog and determine the appropriate dosage.
Regular Veterinary Checkups
Schedule regular checkups with your veterinarian to monitor your dog’s health and detect any potential issues early on. Early intervention for conditions like hip dysplasia can significantly improve their quality of life.
Final Thoughts
The German Shepherd is a breed that truly embodies the phrase “form follows function.” Its anatomy is a testament to its versatility, intelligence, and physical capabilities. From its well-balance skeletal structure to its powerful muscles, every aspect of its anatomy is designe to enable it to excel in a variety of roles. By understanding and appreciating the fascinating anatomy of the German Shepherd, we can better understand and admire this remarkable breed.









Leave A Comment