Top 6 Tips To Improve Your Dog’s Life With Osteoarthritis

Like us, dogs can face health challenges, including osteoarthritis, which affects their joints and mobility. Osteoarthritis, also known as degenerative joint disease, is a common ailment that can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in dogs.
Watching your furry friend struggle with osteoarthritis can be distressing. But don’t worry, there are plenty of ways to help them live a happier, more comfortable life! Whether it’s through gentle exercises, a balanced diet, or some extra TLC, these top 6 tips will make a world of difference for your dog. Let’s dive in and explore how you can improve your dog’s life with osteoarthritis,
Here Are Six Prime Ideas To Improve Your Dog’s Life With Osteoarthritis
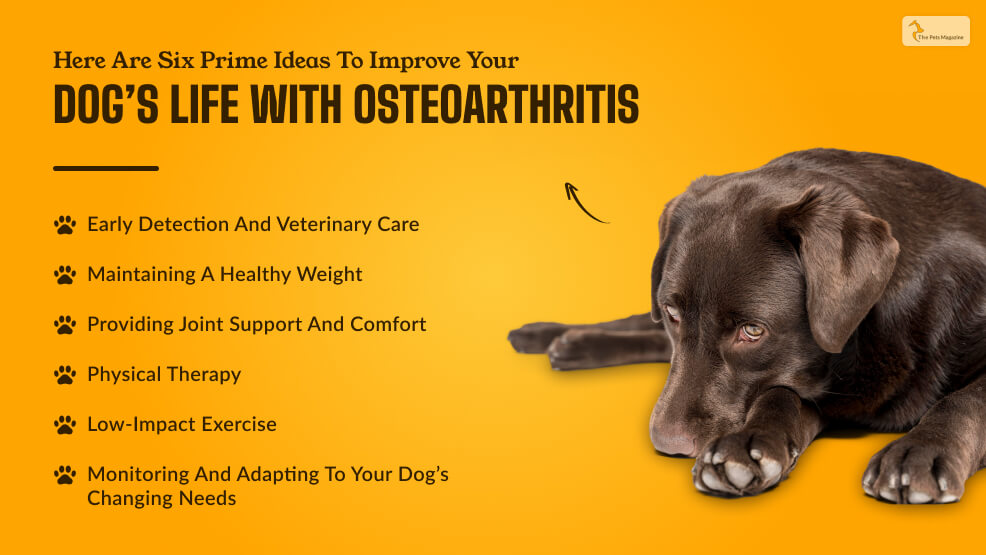
In this guide, we will explore six essential tips to enhance your dog’s life and manage osteoarthritis more effectively. Each tip is carefully curated based on the latest research, expert advice, and the collective experiences of dedicated pet owners who have navigated this challenging journey.
1. Early Detection and Veterinary Care
Identifying the signs of this condition in its early stages allows for timely intervention, enabling a better chance of slowing its progression and minimizing discomfort for your furry companion.
According to the American Kennel Club, the signs of osteoarthritis may include:
- Decreased activity.
- Stiffness.
- Difficulty rising or walking.
- Reluctance to climb stairs or jump.
- Changes in behavior or temperament.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you must schedule a visit to your veterinarian promptly.
During the veterinary examination, the veterinarian will conduct a thorough physical assessment and may order X-rays to evaluate the extent of joint damage. Early detection through X-rays can provide crucial insights into the condition’s severity, allowing for tailored treatment plans.
The veterinarian may prescribe pain medications and joint supplements or recommend lifestyle modifications and a suitable exercise routine. Regular follow-ups with your vet will ensure that the treatment plan remains effective and can be adjusted if necessary.
2. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight places additional stress on the joints, exacerbating the pain and discomfort associated with this condition. By ensuring that your dog maintains an ideal weight, you can significantly improve their mobility and overall quality of life.
Obesity is prevalent among dogs, leading to many health problems, including worsening osteoarthritis. Statista reported that approximately one-fifth (around 19%) of dogs were found to be obese, while a higher proportion (approximately 37%) were categorized as overweight.
To achieve and maintain a healthy weight, you must include a well-balanced diet, portion control, and regular exercise in your dog’s schedule.
Consulting with your veterinarian is vital in determining your dog’s weight and dietary requirements.
3. Providing Joint Support and Comfort
When alleviating the discomfort caused by osteoarthritis in dogs, offering targeted joint support is paramount. Fortunately, advancements in veterinary medicine have introduced effective medications that can significantly improve a dog’s quality of life. Galliprant medication has gained significant popularity in providing joint support and comfort.
Galliprant is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) specifically designed to target pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis. Unlike traditional NSAIDs, Galliprant targets the specific enzyme responsible for inflammation, reducing the risk of side effects often associated with other medications.
However, PetRx warns against administering Galliprant to dogs hypersensitive to Grapiprant or weighing less than 8 lbs. Also, refrain from giving Galliprant if your dog is on aspirin, other NSAIDs, or corticosteroids unless instructed by your vet.
Consulting with your veterinarian to determine if Galliprant is suitable for your dog is essential. The veterinarian will assess your dog’s health, consider any existing medical conditions, and tailor a treatment plan that best suits their needs.
4. Low-Impact Exercise and Physical Therapy
Low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, and controlled play, are gentle on the joints while providing essential cardiovascular benefits.
Based on information from VCA Animal Hospitals, osteoarthritis (OA) affects around 25% of all dogs, regardless of their age. Moreover, approximately 60% of dogs may display x-ray evidence of OA at some point in their lives, making it the most prevalent chronic disease among canines.
Incorporating physical therapy into your dog’s routine can also yield remarkable results in managing osteoarthritis. Techniques like gentle massage, passive range of motion exercises, and balance training can help improve joint function and reduce pain.
Physical therapists can design personalized exercise plans tailored to your dog’s specific needs and limitations.
Here are some low-impact exercises that can help dogs with osteoarthritis:
- Short Walks: Gentle, short walks on soft surfaces like grass can help maintain mobility without putting too much strain on the joints⁴⁵.
- Swimming: The buoyancy of water reduces stress on the joints while providing resistance to help build muscle strength. Swimming or using an underwater treadmill can be very beneficial.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Gently moving your dog’s joints through their full range of motion can help maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Gentle Stretching: Stretching the muscles around the affected joints can improve flexibility and reduce pain.
- Treadmill Walking: If your dog is comfortable with it, walking on a treadmill slowly can be a controlled way to exercise.
- Interactive Play: Using interactive toys or playing gentle games like hide and seek and scent hunts can keep your dog active without high-impact movements. It will also keep your dog mentally stimulated.
Always consult with your veterinarian before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for your dog’s specific condition.
5. Monitoring And Adapting To Changing Needs
As dogs age and their osteoarthritis progress, their needs may change. Therefore, regularly monitoring their condition and being attentive to any alterations in behavior or mobility is crucial. Stay observant for signs of pain, stiffness, or reluctance to engage in regular activities.
Adapting to your dog’s changing needs involves:
- Being flexible with their exercise routine.
- Adjusting their diet.
- Ensuring that the living environment remains comfortable and accommodating.
Consulting with your veterinarian regularly allows for timely adjustments to your treatment plan, including medications and supplements.
Remember, your dog’s well-being is at the core of this journey, and by being proactive in monitoring and adapting to their evolving requirements, you can continue to provide the best possible care for them throughout their life with osteoarthritis.
6. Managing Pain And Discomfort
As a responsible pet owner, it is crucial to prioritize pain management to ensure your furry companions can lead fulfilling lives despite this condition.
Various strategies can be employed to manage pain effectively. Your veterinarian may prescribe pain medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other analgesics, to alleviate inflammation and provide relief. Following your vet’s instructions carefully and monitoring your dog for any adverse medication reactions is essential.
Additionally, complementary therapies, like acupuncture, cold laser therapy, and heat therapy, can offer non-invasive and drug-free pain relief. These alternative treatments can be beneficial in reducing inflammation, stimulating blood flow, and promoting healing in the affected joints.
Alternative Treatments or Therapies for Managing Osteoarthritis in Dogs

There are several alternative treatments and therapies that can help manage osteoarthritis in dogs:
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice can help reduce pain and inflammation by stimulating specific points in the body.
- Cold Laser Therapy: Also known as low-level laser therapy, this treatment uses light to reduce inflammation and pain, and promote healing.
- Hydrotherapy: Swimming or underwater treadmill exercises can help improve mobility and strengthen muscles without putting stress on the joints⁴.
- Massage Therapy: Regular massages can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and alleviate pain.
- Stem Cell Therapy: This involves injecting stem cells into the affected joints to promote regeneration and repair of damaged tissues.
- Shockwave Therapy: This non-invasive treatment uses sound waves to stimulate healing and reduce pain in the joints.
- Dietary Supplements: Supplements like glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids can support joint health and reduce inflammation.
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs, such as turmeric and Boswellia, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help manage arthritis symptoms.
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): This therapy uses electrical impulses to reduce pain and improve mobility.
Improving your dog’s life with osteoarthritis is an ongoing journey that requires dedication, compassion, and a proactive approach. By implementing the six essential tips presented in this guide, you can significantly enhance your furry friend’s quality of life and alleviate the challenges associated with this condition.
Remember, every dog is unique, and finding the right combination of strategies that suit your dog’s specific needs may take time and patience. Working closely with your veterinarian and staying attuned to your dog’s behavior will ensure you provide the best care possible.
Read Also:









Leave A Comment