Everything You Need to Know About Hookworm in Dogs: A Comprehensive Guide


As a responsible dog parent, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential health risks your furry friend may face, including the dreaded hookworm infection. Hookworms are parasitic worms that can wreak havoc on your dog’s wellbeing if left unchecked.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of hookworms, exploring their nature, the signs and symptoms of infection, effective treatment options, and, most importantly, how you can prevent your beloved pup from falling victim to these pesky parasites.
What Are Hookworms and How They Infect Dogs

Hookworms are small, blood-feeding parasites that live in the small intestine of dogs. These worms latch onto the intestinal wall and feed on your dog’s blood, causing various health problems. Dogs can become infected with hookworms in several ways, including:
- Ingesting hookworm larvae from contaminated soil or surfaces
- Penetration of hookworm larvae through the skin
- Consuming infected prey, such as rodents or birds
- Transmission from an infected mother to her puppies, either in utero or through nursing
Understanding how these parasites spread is crucial in developing an effective prevention and management strategy.
Hookworm Infection in Puppies and Its Impact
Puppies are particularly susceptible to hookworm infections, which can be transmitted from an infected mother during pregnancy or through nursing. Hookworm infections in puppies can be especially problematic, as the parasites can cause severe anemia, stunted growth, and even death if left untreated. Early detection and prompt treatment are essential to ensure the health and well-being of your new furry family member.
Can Hookworms Be Transmitted to Humans?
Yes, hookworms can be transmitted from dogs to humans, particularly through skin contact with contaminated soil or surfaces. However, human hookworm infections are relatively uncommon and can be prevented by practicing good hygiene and avoiding direct contact with areas that may be contaminated.
Signs and Symptoms of Hookworm Infection in Dogs
Hookworm infection can manifest in a variety of ways, and the severity of symptoms often depends on the number of worms present and the overall health of your dog. Common signs of hookworm infection include:
- Diarrhea, often with blood or mucus
- Weight loss and poor appetite
- Anemia due to blood loss
- Lethargy and weakness
- Rough or dull coat
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Coughing or difficulty breathing in severe cases
It’s important to watch for these symptoms and seek veterinary attention promptly if you suspect your dog may be infected.
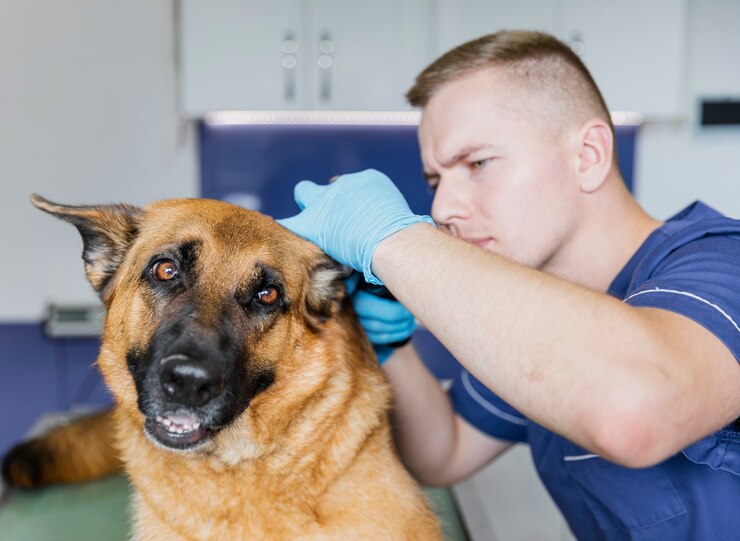
Diagnosing Hookworm Infection in Dogs

Diagnosing hookworm infection typically involves a fecal examination, where your veterinarian will analyze a sample of your dog’s stool for the presence of hookworm eggs. This simple test can provide a definitive diagnosis and guide the appropriate treatment plan.
In some cases, your veterinarian may also recommend additional tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) or biochemistry panel, to assess the overall health of your dog and the extent of the infection.
Treatment Options for Dogs with Hookworms
If your dog is diagnosed with hookworms, your veterinarian will prescribe a course of deworming medication to eliminate the parasites.
Common dewormers used to treat hookworm infections include:
- Fenbendazole
- Pyrantel pamoate
- Mebendazole
- Ivermectin
These medications work by disrupting the lifecycle of the hookworms, causing them to detach from the intestinal wall and be expelled from your dog’s body. In severe cases, your veterinarian may also recommend supportive care, such as fluid therapy or iron supplements, to address any secondary health issues caused by the infection.
The treatment duration for hookworm infection in dogs can vary depending on the severity of the infection and your dog’s response to the prescribed deworming medication. Typically, a course of deworming medication lasts 2-4 weeks, with follow-up treatments as needed to ensure the complete elimination of the parasites.
Preventing Hookworm Infection in Dogs

Preventing hookworm infection in your dog is a multi-faceted approach that involves a combination of environmental management and regular veterinary care. Here are some key steps you can take:
- Maintain a Clean Environment: Regularly clean and disinfect your dog’s living area, including their bedding, toys, and outdoor spaces where they spend time. This helps to eliminate any hookworm larvae or eggs that may be present.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly after handling your dog or cleaning up after them, and avoid allowing your dog to lick your face or hands.
- Provide Routine Deworming: Work with your veterinarian to establish a regular deworming schedule for your dog, typically every 3-6 months, to keep hookworms and other parasites at bay.
- Limit Outdoor Access: Restrict your dog’s access to areas that may be contaminated with hookworm larvae, such as public parks or areas with high concentrations of animal waste.
- Monitor for Signs of Infection: Regularly check your dog for any signs of hookworm infection, such as diarrhea or poor coat condition, and seek veterinary attention if you notice any concerning symptoms.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of your dog developing a hookworm infection.
Can My Dog Get Reinfected With Hookworms?
It is possible for dogs to become reinfected with hookworms if they are exposed to contaminated environments or if the initial treatment is not fully effective. Maintaining a regular deworming schedule and practicing good hygiene and environmental management can help prevent reinfection.
Importance of Regular Deworming for Dogs
Regular deworming is a crucial component of maintaining your dog’s overall health and preventing parasitic infections, including hookworm. Dewormers work by eliminating any existing parasites and interrupting their lifecycle, preventing reinfection. Your veterinarian can recommend the appropriate deworming schedule and medication based on your dog’s age, health status, and risk factors.
Potential Complications of Hookworm Infection in Dogs
While hookworm infections can be effectively treated, they can also lead to serious complications if left unchecked. Some potential complications include:
- Severe Anemia: Hookworms feed on your dog’s blood, which can lead to life-threatening anemia, especially in young, old, or already weakened dogs.
- Intestinal Blockage: In rare cases, many hookworms can cause an intestinal blockage, requiring immediate veterinary intervention.
- Malnutrition: The blood loss and poor nutrient absorption caused by hookworms can lead to malnutrition and weight loss.
- Organ Damage: Severe or prolonged hookworm infections can cause damage to the intestines, liver, or other vital organs.
Recognizing and addressing these potential complications early on is crucial for your dog’s health and well-being.
How to Properly Clean and Sanitize Your Home to Prevent Hookworm Transmission

Maintaining a clean and sanitized environment is essential in preventing the spread of hookworm infections. Here are some key steps you can take to keep your home and yard free of hookworm larvae and eggs:
- Vacuum Regularly: Use a vacuum with a HEPA filter to thoroughly clean carpets, rugs, and upholstered furniture, where hookworm larvae and eggs may accumulate.
- Disinfect Surfaces: Regularly clean and disinfect hard surfaces, such as floors, walls, and countertops, using a pet-safe disinfectant or a solution of bleach and water.
- Dispose of Waste Properly: Promptly clean up and properly dispose of your dog’s feces, as this is a common source of hookworm contamination.
- Maintain Outdoor Areas: Keep your yard clean and free of debris, and consider treating the soil with a larvicide to kill any hookworm larvae that may be present.
- Wash Bedding and Toys: Regularly wash your dog’s bedding, toys, and any other items they come into contact with using hot water and a pet-safe detergent.
By implementing these cleaning and sanitization practices, you can create a safer, hookworm-free environment for your beloved canine companion.
To ensure the continued health and wellbeing of your canine companion, consider scheduling a consultation with your veterinarian today.
They can provide personalized guidance on the best deworming and prevention strategies for your dog, as well as address any other concerns you may have. Don’t wait – take proactive steps to keep your furry friend happy and hookworm-free!









Leave A Comment