Is Glucosamine Good for My Dog? Benefits and Usage Explained


Health and comfort are a pet owner’s top priorities. So, from here that discussion about canine supplementation begins, be it an aged dog or joint-related issues dog; glucosamine comes into mind. Does your dog require glucosamine?
We will try our best to put down here all the little details you might want to know about it, from its advantages to use, its dosages, possible side effects, and most frequently asked questions.
History of Glucosamine and Its Uses in Veterinary Science
It is a natural chemical produced by the body itself, as in the case of cartilage. It is that special tissue that acts like cushioning around joints.
Veterinary medicine has taken active notice of the role of glucosamine in maintaining healthy joints and, thereby, Osteoarthritis.
Glucosamine maintains the integrity of the cartilage structures, decreases inflammation, and may retard degenerative processes in the joints. Glucosamine is one of the cornerstones in treating joint disorders in dogs.
What Is Glucosamine?
Glucosamine is an amino sugar that may isolate from the shell of shellfish or synthesize in the laboratory. These supplements are typically compounded with chondroitin sulfate, MSM, or hyaluronic acid for animal joint maintenance.
Types of Glucosamine
Here are a few types of glucosamine are using for animal supplements:
Glucosamine Sulfate
It is the most bioavailable and active glucosamine for cartilage support. Now, there is just a little bit of that. Minus the sulfur there, it does not remotely compare to this as a good cartilage preservative.
N-acetyl-glucosamine (NAG)
That one is using a lot more for other kinds of connective tissues and digestion. It’s not nearly as useful for any joint health in that regard. Each has its features, so sometimes, the selection depends on the requirements of your dog and even on your vet’s advice.
Traditional Uses of Glucosamine on Dogs
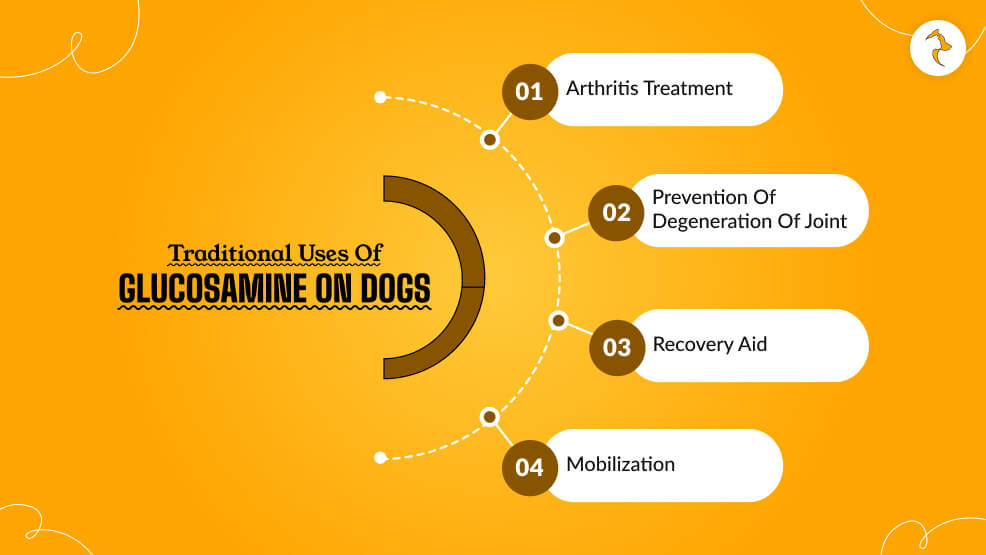
Glucosamine is a remedy for most joint and mobility diseases. Among the most frequently used ones include:
1. Arthritis treatment
It prevents inflammation in the regrowth of cartilage. It is one of the major constituents in the treatment of Osteoarthritis, a degenerative disease causing much pain in the joints, sometimes stiffness, and limping often.
2. Prevention of Degeneration of Joints
This prevents long-legged breeds, sporting breeds, and dogs prone to hip dysplasia. Ultimately, it saves the wear and tear of cartilage over time.
3. Recovery Aid
Some of the applications of glucosamine are as described above. These dogs are put in glucosamine treatment, recovering from orthopedic surgery or injuries like torn ligaments. The supporting repairing system enhances speeding up their recovery.
4. Mobilization
Geriatric dogs or dogs with any form of disorder in their joints will never walk again. Glucosamine increases the lubrication process of the joint, and it will make easy mobility around the body comfortable.
Dosage and Administration
This will determine the correct dosage of glucosamine as it can safely administer and effectively prescribe. Prescriptions are set by your dog’s weight, age, and actual health condition he or she is suffering from. These are the basic recommended dosages:
- Small breeds: less than 25 pounds: 250-500 mg/day.
- Medium breed dogs: those with a weight range of 25 to 50 pounds: 500-1,000 mg/day.
- For larger dogs: weighing 50-100 lbs, 1,000-1,500 mg/day.
- For large breeds: over 100 pounds, 1,500-2,000 mg/day.
Dosage Routes
Glucosamine is available in many preparations:
- Orally administrable in tablets, which are available chewable for administration convenience, often flavored.
- Liquid formulation mixed directly with their meals.
- Powder for topping food
- Flavored dental treats the fussy dogs go crazy over, talk to the manufacturer and vet. Which works best, form or dosing.
Side Effects of Glucosamine
Glucosamine is safe for dogs; some dogs display mild side effects. Here are some the glucosamine side effects of these include the following:
- Gastrointestinal upset: Diarrhea, vomiting, or loss of appetite.
- Fatigue or lethargy: Dogs become less energetic while on the drug.
- Allergic reactions: These are rare but can be expected, especially in dogs with a shellfish allergy to glucosamine.
If such side effects worsen or prolong, use should stop, and the veterinarian should consult.
Precautions and Interactions
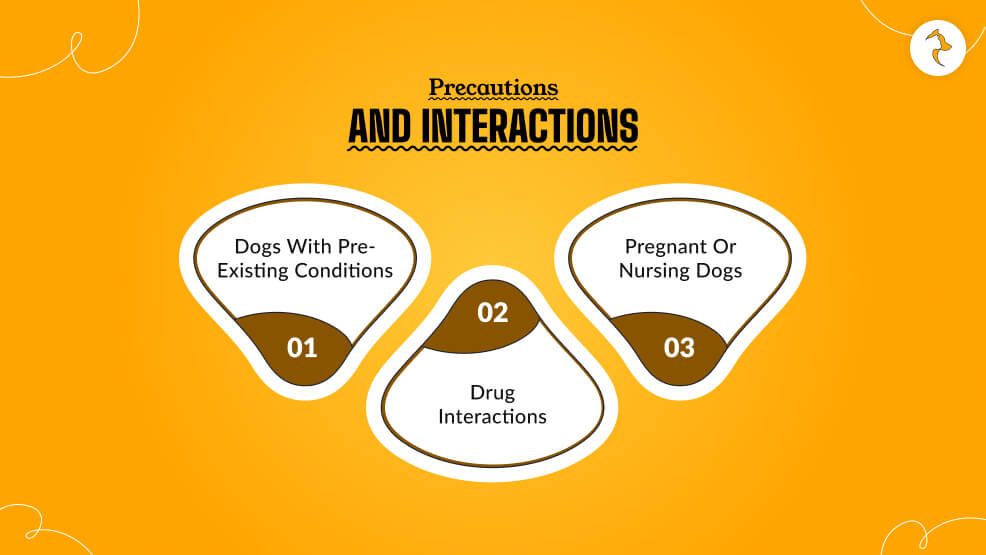
Here are a few precautions and interactions when it comes to giving Glucosamine for dogs.
1. Dogs with Pre-Existing Conditions
- Diabetes: Glucosamine can alter blood sugar, so dogs with this disease should be kept under constant monitoring.
- Organ disease: When your dog has organ disease, always consult your veterinarian before using glucosamine.
- Bleeding disorders: Glucosamine influences the blood’s ability to clot in sensitive breeds.
2. Drug Interactions
Ensure that your veterinarian is well aware of medications and supplements in your dog. This way, they can make sure to prevent any possible interference. For example, glucosamine enhances anticoagulants.
3. Pregnant or Nursing Dogs
Glucosamine safety has not been well studied regarding pregnant or nursing dogs. Please discuss the use with your veterinarian.
Alternative of Glucosamine

Glucosamine cannot be used on your dog. So here the following supplements use to ensure that your dog will have healthy joints:
- Chondroitin Sulfate: This is another supplement to be used with glucosamine. The latter nutrient somehow blocks cartilage degradation.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These are chemicals present in fish oil and also cause inhibition of inflammation. The joint fluidity increases as well.
- Turmeric (Curcumin): This is an anti-inflammatory and may have the effect of improving joint pain.
- Green-Lipped Mussel (GLM): This is a nutrient-rich supplement that helps to maintain joint health.
- Physical Therapy: Exercise, hydrotherapy, and massage improve movement and reduce pain.
Wrapping Up!
A glucosamine supplement can help maintain and prevent joint issues in dogs if applied correctly to what your pet may need.
A visit to your veterinarian is in order any supplement to understand what would be advised. In this case, the right way will pave the way for a much more pain-free life for your dog.
Dosage: The dosing in a dog differs greatly with its size and level of health. The dosage for small dogs tends to be intermediate, taken daily, 250 to 500mg.
On the shape of the canine’s body, size, 500- to 1,000mg, 1,000-1,500, and 1,500-to 2,000mg be administered. To consult with the veterinarian for an appropriately recommended dose in your pet’s case, summarize.
Dogs’ glucosamine supplements can be found anywhere in pet shops. One can have it in a pet store, veterinary clinic, and online stores; just make sure to get only the best quality, for our dogs.
Glucosamine supplements are used to for other illness as well, such as,
‣ Glucosamine Helps with Joint Health
‣ Reduces the development of Osteoarthritis
‣ Protects against Damage of Cartilage
‣ Support mobility
‣ Orthopedic surgeries or injuries recover faster.
Human glucosamine is just a small cousin but a different concentration and formula. Hummable glucosamine contains poison for dogs. When presenting it before your vet, beware and get the glucosamine product meant for pets.









Leave A Comment