Prednisone for Dogs: A Critical Review of Pros and Cons


Prednisone is one of the most widely prescribe drugs in veterinary medicine. The medicine is use for the treatment of a wide array of canine diseases. It is a medication that falls in the category of corticosteroids.
Corticosteroids are synthetic analogs of naturally occurring hormones produced by the body’s adrenal glands. While Prednisone can be quite effective in treating most conditions, pet owners need to know how it works, proper dosing, side effects, and precautions.
In this context, a complete guide to Prednisone in dogs is provided with benefits, risks, and tips on administration.
Overview of Prednisone and Common Veterinary Medication Uses

This is one of the most often give drugs in veterinary medicine since the drug can administer for any reason listing above.
Either to reduce inflammation, inhibit a dog’s immunity, or assist in controlling some chronic disease.
Dogs can be given Prednisone to treat reactions, autoimmune diseases, inflammation, and some cancer conditions. It makes it available for veterinarians in tablets, liquid, and injectable form.
Although highly effective, Prednisone should be administered with close observation because the potential for adverse effects is often directly proportional to its duration of use.
What is Prednisone?

Prednisone is a synthetic corticosteroid. Like the endogenously produced cortisol, it exerts its effect on the body to modulate such processes as immune function and inflammatory responses, for example, but also affects metabolic mechanisms.
The corticosteroid mainly acts by reducing or inhibiting inflammation and suppressing the immune response to treat patients with excessive, inappropriate immune system reactions or significant inflammatory responses in the body.
It is not a root problem but may help manage signs and enhance a dog’s well-being. Veterinarians prescribe Prednisone if alternative therapies fail or from inflammation-induced distress or health damage to your dog.
General Applications of Prednisone for the dogs
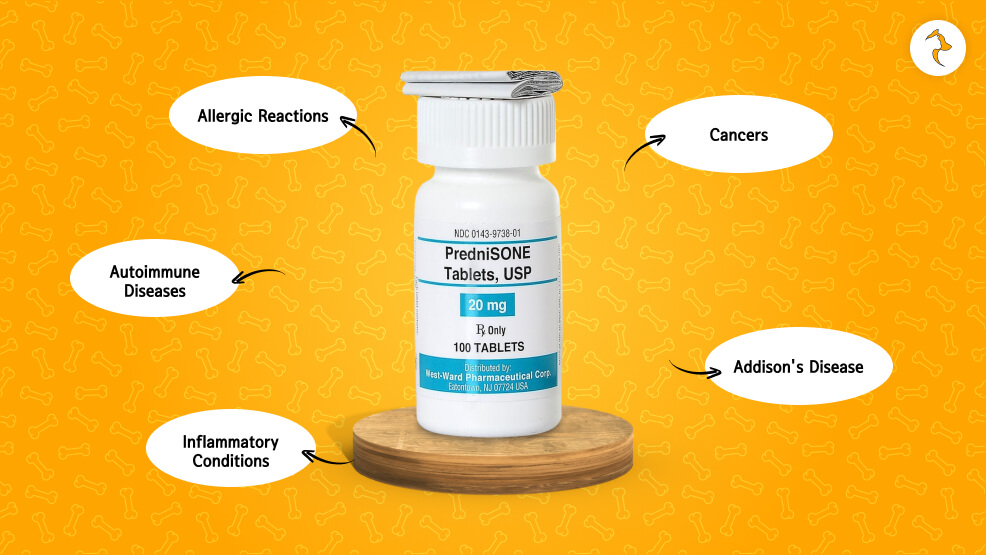
Prednisone acts to cure some medical conditions affecting your dog.
Allergic Reactions
Prednisone is used as a medication to treat severe allergic reactions or inflammation arising from allergic dermatitis, flea allergy, or food allergy. This helps reduce itchiness, inflammation, and redness.
Autoimmune Diseases
In this case, the immune system is attacking tissues in the body, and the administration of Prednisone could control the response by reducing inflammation of the immune system. Some of the examples of this include AIHA and IMT.
Inflammatory Conditions
It is prescribed for conditions like arthritis, IBD, and all inflammatory conditions, which are the reason for pain and uneasiness.
Cancers
Sometimes, Prednisone is used as a component in cancer therapy. Hence, it makes the condition easier by removing the inflammation.
Addison’s Disease
Those dogs that are supposed to produce a reduced level of cortisol, such as dogs affected with Addison’s disease, require prednisone replacement so that their bodily functions may not be adversely altered.
Dosage and Administration

The dosage of Prednisone for dogs varies according to the conditions, degrees of severity, and weight of dogs.
Prednisone usually initiates with a certain dose and tapers gradually over weeks, depending on the response of the patient.
Average Dosage Ranges by Weight and Condition
Initially, some vets administer much higher doses if the diseases are from severe allergy to autoimmune to inflammation. Some even use 0.5 to 2 mg body weight per pound each day in one or twice division.
Maintenance or Tapering Dose
The dose is tapered down once the dog’s symptoms have disappeared. This is very important because tapering down the dose helps avoid the negative effects of withdrawal and helps the body to adjust to it gradually.
Most times, the dose must reduce by small increments every few days or weeks according to the dog’s state.
For example,
A 20-pound dog begins on 10 to 40 mg of Prednisone a day, which can be tapered slowly while continuing treatment.
Forms of Prednisone
There are various forms of Prednisone, including the following:
- Oral tablets: This is the most common form administer orally once or twice daily.
- Liquid Prednisone: For dogs in case, they cannot consume the medication in its oral form. A syringe or dropper administered the liquid dosage.
- Injectable: The medication can also come in the injectable form if they are ailing or in an oral form. The veterinarian in that scenario utilizes the Prednisone clinically only to bring quick relief to dogs.
How to Administer Prednisone for Dogs
Always adhere to your veterinarian’s prescription on the dosage and rate of administration. Prednisone should not stop abruptly because it causes withdrawal symptoms and disrupts the natural production of hormones in a dog’s body.
Administration with Food
Giving Prednisone tends to irritate the stomach; thus, it is typically advisable to take it with food to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort.
Consistency
If your dog is to remain on long-term prednisone treatment, it is best to try and receive this medication at about the same time each day so that levels in the system are kept as consistent as possible.
Monitor Side Effects
Pay attention to any behavioral or physical changes your dog exhibits. Contact your vet immediately if you notice any of the following symptoms.
Possible Side Effects
Although Prednisone has many benefits, it is not without a few disadvantages either. Some of the most common side effects are as mentioned below:
Increased Thirst and Urination
Prednisone makes your dog drink more water than normal and urinate.
Increased Appetite
Most dogs on Prednisone display a sharp increase in appetite that leads to weight gain if it is not controlled properly.
Purring
Animals start extreme panting without any reason for heat or exercise for this.
Behavior
Dogs show typical behavior changes when anxious and become aggressive or irritable sometimes. Some other less-known symptoms might also be there.
Gastrointestinal Upset
Long-term use of Prednisone is considered to affect the stomach by developing ulcers or irritation due to this hormone; sometimes, they can also express vomiting and diarrhea.
Debilitated Immune Condition
This hormone is involved in the suppression of immune conditions. As a result, long-term exposure makes the dogs prone to major infections.
Possible Reactions of Prednisone on Dogs
Discuss the following conditions with your vet before giving Prednisone to your dog, in case your dog suffers from any of the following: diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease.
Medical conditions alter with this medication. The dosages could need adjustment, so an increase in monitoring could be required.
- Drug Interactions: Prednisone interacts with different drugs like NSAIDs, some antibiotics, and diuretics. Other medication that your pet takes to be told to the vet.
- Never withdraw the patient abruptly: Some withdrawal symptoms may cause severe complications. It must taper off very gradually, instructed by your veterinarian.
Alternatives of Prednisone
Another alternative Prednisone can be provided for your dog in case of such serious side effects. Other alternatives include:
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Other drugs like Rimadyl and Meloxicam can relieve your dog’s arthritis or musculoskeletal injuries with their pain and inflammation.
- Immunosuppressive Medications
If there are autoimmune conditions, one may use drugs like azathioprine or cyclosporine instead of Prednisone.
- Natural Supplements
Some supplements, like omega-3 fatty acids or turmeric, can be useful as anti-inflammatory agents but should only be given under the guidance of a veterinarian.
Can I Give My Dog Benadryl Instead of Prednisone?
Benadryl, or diphenhydramine, is an antihistamine for allergic reactions in dogs. In most cases, it usually helps mitigate most mild allergies.
Thus, is never a replacement for Prednisone, especially when inflammation is severe, and the case with autoimmune disorders.
Benadryl may quell itching and swelling, but the effects cannot match Prednisone, which, besides anti-inflammatory immunosuppression. Always seek your veterinarian to know any form of medication changes.
Wrapping Up!
Prednisone is one of the drugs used in treating many conditions in dogs. The benefits of using this drug include reducing inflammation and managing autoimmune diseases.
However, due to the possible side effects of Prednisone, its use needs to be strictly monitored. No matter how mild, any drug must always be given under the doctor’s prescription regarding the dosage and administration and monitored closely by your dog.
You then assist your dog in living more comfortably, in a healthier life, and probably a safer one with fewer dangers tied to using Prednisone.









Leave A Comment